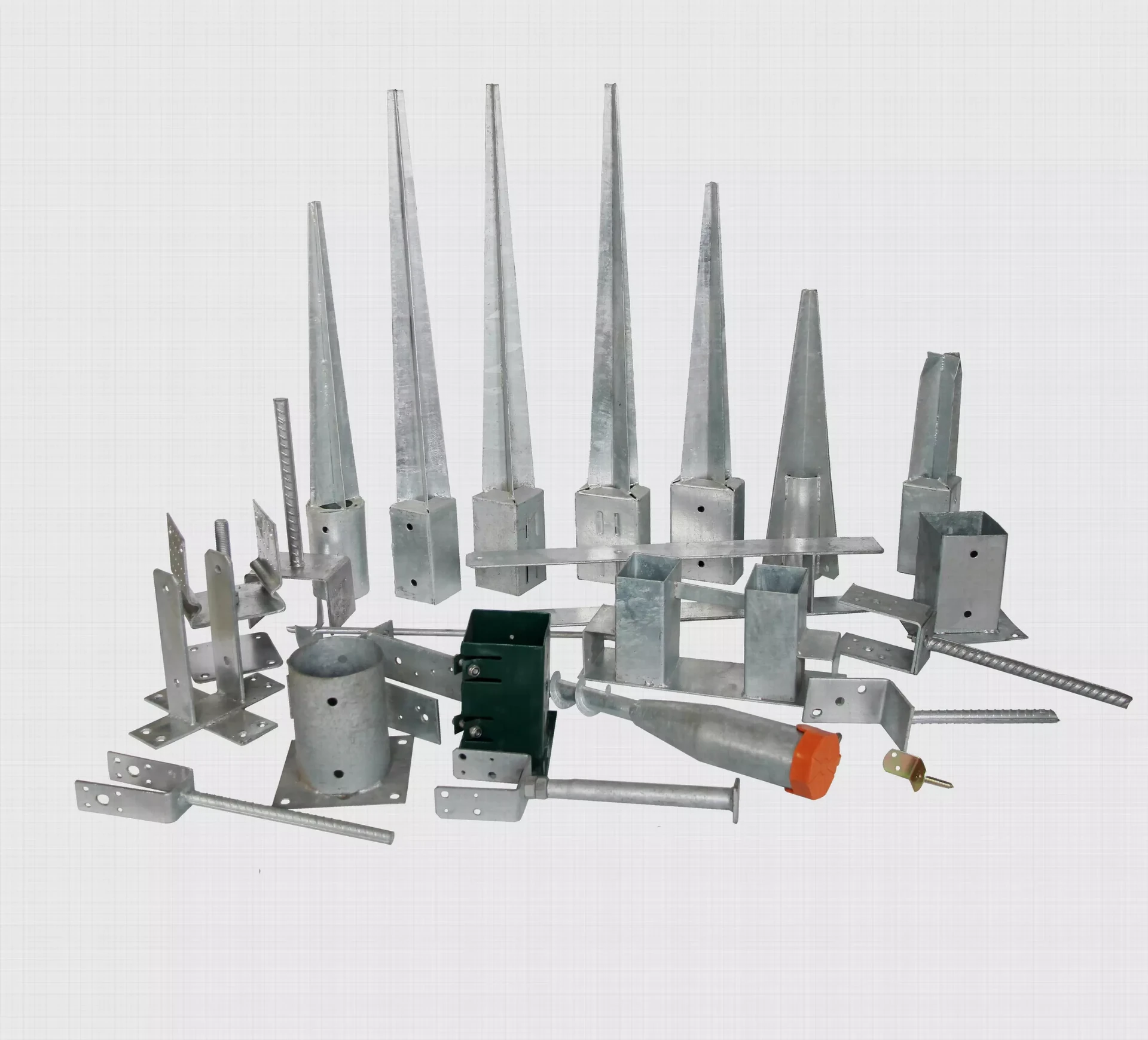
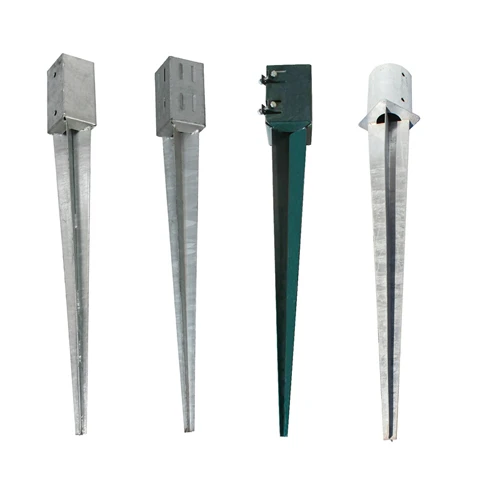
Power Pole Anchors Essential Elements for Reliable Electrical Supply
In the world of electricity distribution, the infrastructure that supports the transmission of power plays a crucial role. One of the most vital components in this system is the power pole anchor. These anchors ensure the stability and longevity of the poles that carry the wires and equipment necessary for distributing electricity to our homes and businesses. This article delves into the significance of power pole anchors, their types, installation methods, and the impacts of their proper use on electrical distribution systems.
Understanding the Importance of Power Pole Anchors
Power poles are typically tall structures that support electrical lines. They are exposed to various forces, including wind, ice accumulation, and the weight of the electrical lines. Without proper anchoring, these poles can lean, tilt, or even topple over, leading to power outages and potential hazards. Power pole anchors are designed to counteract these forces, providing stability and ensuring that the poles remain upright under challenging conditions.
Anchoring systems generally consist of rods, cables, or concrete blocks that are embedded in the ground. These components are strategically placed to distribute the load and keep the pole secure. The design of these anchors varies based on the environmental conditions and the specific requirements of the electrical distribution system.
Types of Power Pole Anchors
There are several types of power pole anchors, each suited for different applications
1. Deadman Anchors These are often used in high-load situations. A deadman anchor consists of a large concrete block or a buried heavy object that prevents the pole from moving. This type of anchor is particularly effective in areas with high wind loads or where the soil composition is loose.
power pole anchor

2. Guy Wire Anchors Guy wires are tensioned cables that stabilize the power poles. They are anchored to the ground through various methods, such as eye bolts, concrete anchors, or auger anchors. The use of guy wires is common in areas with heavy ice loads or where additional lateral support is necessary to keep the poles upright.
3. Auger Anchors These are screw-like devices that are drilled into the ground. Auger anchors are effective in providing strong resistance against both vertical and lateral forces. Because they are installed by rotating into the soil rather than digging, auger anchors tend to disturb the soil minimally and maintain the integrity of the surrounding area.
4. Helical Anchors Helical anchors have a similar design to auger anchors but feature helix-shaped blades that allow for better load distribution. These anchors provide strong resistance and are typically used in applications where soil conditions are poor or where additional support is required.
Installation and Maintenance of Power Pole Anchors
Proper installation of power pole anchors is critical to their performance. This process involves evaluating the soil conditions, determining the type of anchor to be used, and selecting the right configuration. It often requires specialized equipment and trained personnel to ensure that the anchors are installed correctly and securely.
Once installed, regular maintenance is essential to ensure that power pole anchors continue to perform effectively. This includes periodic inspections to check for signs of wear or damage, as well as assessing the soil conditions around the anchors. Maintenance is especially important in regions prone to extreme weather conditions, which can significantly affect the stability of power poles.
Conclusion
Power pole anchors are indispensable for the safe and reliable distribution of electricity. They provide the necessary support to keep power poles stable despite environmental challenges. By understanding the types of anchors available, their installation methods, and the importance of regular maintenance, utilities can ensure the integrity and reliability of their electrical distribution systems. In an age where uninterrupted power supply is essential for daily activities, investing in quality anchoring systems is not just a best practice; it’s a necessity for fostering a resilient electrical infrastructure.