Understanding Anchors for Electric Poles A Foundation of Stability
Electric poles are an essential component of modern infrastructure, enabling the distribution of electricity across vast distances and ensuring that homes, businesses, and industries remain powered. However, the effectiveness and longevity of these poles heavily depend on their proper installation and the use of appropriate anchoring systems. This article will delve into the significance of anchors for electric poles, their types, installation procedures, and best practices.
Importance of Anchors
Anchors play a crucial role in stabilizing electric poles, especially in areas prone to strong winds, heavy storms, or seismic activities. A well-anchored pole can withstand environmental stresses, preventing it from toppling over and disrupting the electricity supply. This becomes even more critical in rural areas where poles often stand alone and can be affected by external forces with little support from surrounding structures.
When electric poles are installed, engineers must consider the soil conditions, moisture levels, and potential load factors that will influence the pole's stability. Proper anchoring minimizes the risk of tilt, sway, and eventual failure, ultimately ensuring the safety of the public and the integrity of the power grid.
Types of Anchors
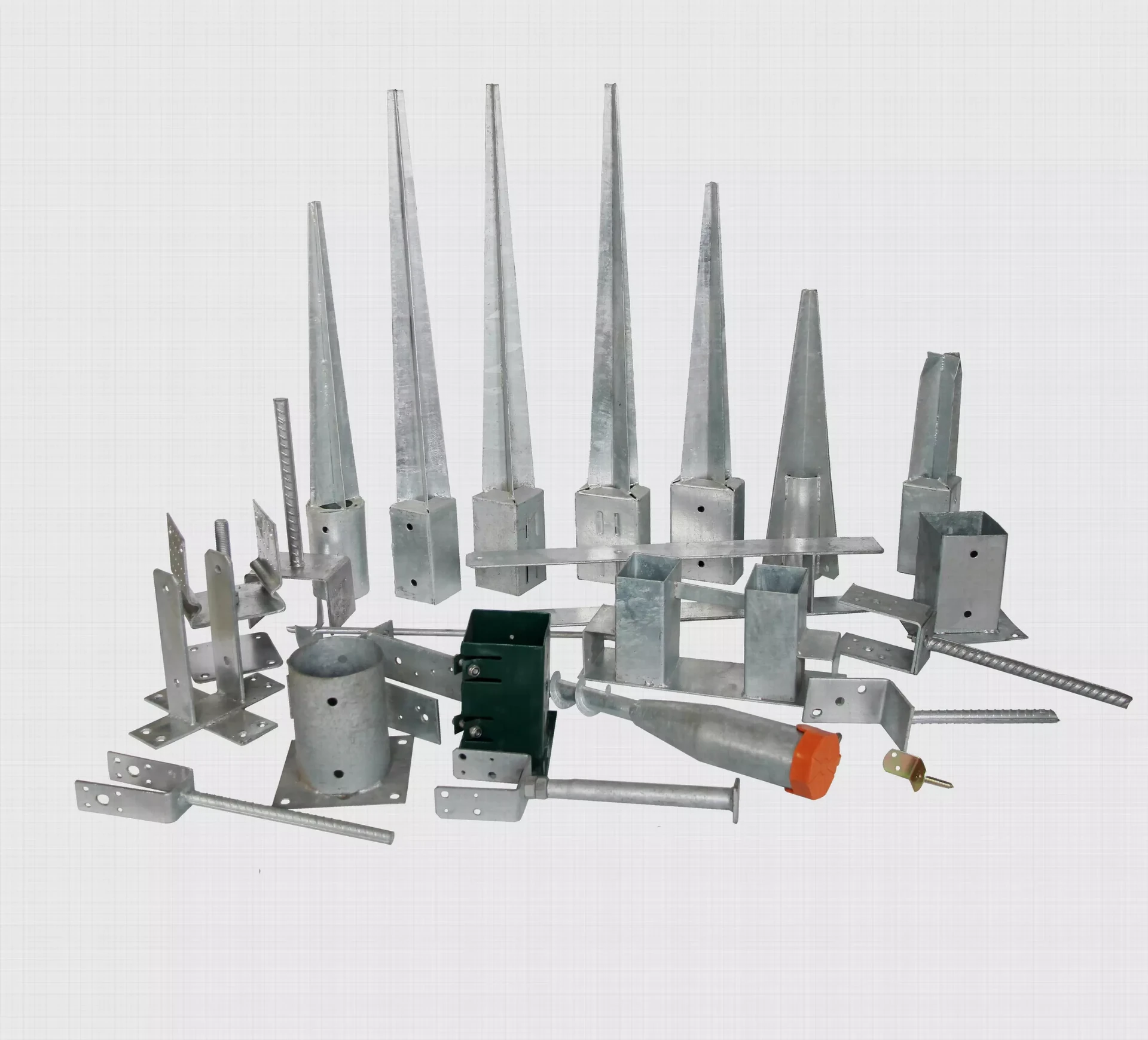
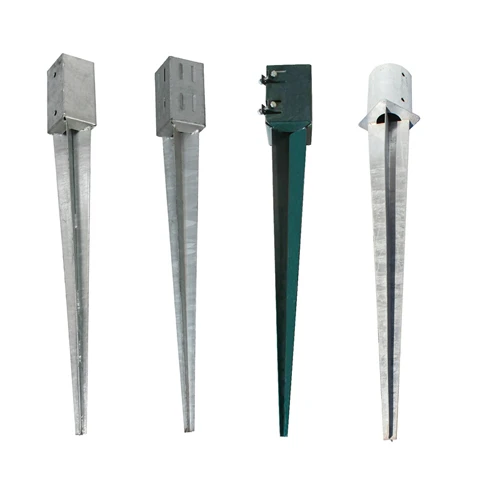
There are several types of anchors used for electric poles, with each designed to withstand different environmental conditions
1. Direct Buried Anchors These anchors are buried directly in the soil, providing resistance against lateral forces. They are often used in areas with stable soil conditions, where the ground does not shift significantly.
2. Concrete Block Anchors Utilized in locations where extra stability is necessary, these anchors involve burying a concrete block that provides additional weight and resistance.
3. Deadman Anchors These anchors consist of large weights or concrete slabs buried below the surface, providing a strong hold for poles that face extreme conditions such as high winds or heavy snowfall.
4. Helical Anchors Often used in softer soils, helical anchors are twisted into the ground and provide excellent resistance to uplift forces. They are particularly useful in areas where traditional anchoring methods may fail.
anchor for electric pole

Installation Procedures
The installation of anchors for electric poles requires careful planning and execution. Engineers must first assess the installation site, taking soil samples and analyzing the environmental conditions. After determining the type of anchor to be used, the following general steps are typically followed
1. Site Preparation Clearing vegetation and debris to ensure a clean working area.
2. Excavation Digging the appropriate holes for the anchor installation based on the chosen type.
3. Anchor Placement Installing the anchor at the recommended depth and ensuring it is positioned correctly for optimal stability.
4. Backfilling Filling the excavated area around the anchor with soil or concrete, ensuring no voids that could lead to shifting over time.
5. Testing Conducting stability tests to confirm that the pole and anchor system can withstand the expected loads.
Best Practices
To ensure the longevity and reliability of electric poles, it's essential to adhere to best practices concerning anchor installation and maintenance. Regular inspections should be conducted to identify any signs of wear, corrosion, or soil erosion around anchors. Investing in high-quality materials and following established guidelines can significantly enhance the performance of anchoring systems.
In conclusion, anchors for electric poles are fundamental to the stability and reliability of electricity distribution networks. By understanding their importance, types, and installation methods, we can better appreciate the engineering efforts that go into maintaining the power infrastructure we often take for granted.